- Home
- »
- Plastics, Polymers & Resins
- »
-
Compostable Multilayer Films Market, Industry Report, 2030GVR Report cover
![Compostable Multilayer Films Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Compostable Multilayer Films Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Material Type (PLA, PHA, Starch-based Films, Cellulose-based Films), By Application (Food Packaging, Personal Care, Pharmaceuticals, Agriculture), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2025 - 2030
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-554-7
- Number of Report Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Bulk Chemicals
Compostable Multilayer Films Market Trends
The global compostable multilayer films market size was estimated at USD 1.42 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.7% from 2025 to 2030. Growing consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging is pushing brands to adopt compostable multilayer films. Companies are using this shift to strengthen their sustainability image and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers, thus boosting the product demand.

A prominent trend reshaping the compostable multilayer films industry is the rapid advancement and incorporation of high-barrier biopolymer technologies into film structures. Manufacturers are shifting focus toward developing compostable alternatives that can offer moisture, oxygen, and UV resistance comparable to conventional multilayer plastics.
Innovations in materials like PLA, PBS, and PHA, when coupled with cellulose-based coatings or nanoclay reinforcement, are enabling performance parity with fossil-based counterparts in packaging for snacks, dairy, and perishable goods. This trend signifies a pivot from basic biodegradability to functional sophistication, targeting a broader application spectrum while staying within the boundaries of compostability certifications such as EN 13432 and ASTM D6400.
Drivers, Opportunities & Restraints
The global regulatory landscape is intensifying its stance against single-use and non-degradable plastic materials, acting as a strong catalyst for compostable multilayer films. Policies such as the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive, California’s SB 54 legislation, and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) frameworks are compelling packaging converters and brand owners to urgently transition toward compostable alternatives.
In particular, multilayer applications-previously exempt from sustainable substitutions due to technical limitations-are now in the crosshairs of sustainability mandates. Compostable multilayer films, offering both environmental compliance and consumer acceptability, have emerged as a viable solution to address these growing regulatory imperatives, thus driving their adoption across the food service, FMCG, and agriculture sectors.
One of the most strategically significant opportunities lies in the parallel development of industrial composting infrastructure in fast-growing economies such as India, Brazil, and Southeast Asian nations. These regions are experiencing a dual dynamic: increasing urban consumption and waste generation alongside supportive government initiatives to build circular economies.
Investments in composting facilities, coupled with public-private partnerships and green municipal policies, are laying the groundwork for scalable end-of-life treatment of compostable materials. This infrastructural momentum is unlocking downstream viability for compostable multilayer films, particularly in sectors like food packaging, where organic waste and its containment can now be processed together. The localization of such ecosystems is poised to substantially elevate market penetration in these high-potential regions.
Despite their environmental appeal, compostable multilayer films industry face critical challenges in balancing cost-efficiency and performance standards. These films often come at a premium-ranging from 1.5x to 3x the price of traditional plastic films-due to the complex formulation and limited production scale of bio-based polymers. Moreover, achieving the mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and barrier performance needed for high-speed packaging lines remains a hurdle.
For brands operating in cost-sensitive segments, especially in mass-market food and consumer goods, the switch to compostable alternatives can lead to operational bottlenecks and increased packaging costs. This performance-cost friction continues to restrain widespread commercial adoption, particularly where regulatory enforcement or consumer pressure is insufficient to offset the premium.
Material Type Insights
Based on material type, the polylactic acid (PLA) segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 43.86% in 2024. Polylactic Acid (PLA) has emerged as the most commercially viable compostable polymer within multilayer film structures due to its established production scale, favorable mechanical properties, and cost competitiveness.
A key driver for PLA is the continuous investment in upstream fermentation technologies and downstream compounding capabilities, particularly across North America, Europe, and Asia. Companies like NatureWorks and Total Corbion are expanding PLA capacities and improving polymer grades with enhanced thermal resistance and barrier properties to meet the requirements of multilayer food and retail packaging.
Moreover, the increasing availability of feedstock from non-GMO corn and sugarcane sources is reinforcing the material’s sustainability credentials, making it a preferred substrate for converters under pressure to deliver certified compostable and high-performance films.
A distinctive growth driver for the PHA-based multilayer film segment is its innate ability to biodegrade in a wider range of environments-including marine, soil, and home composting conditions-without leaving toxic residues. This advantage is gaining strategic relevance as global regulatory frameworks evolve beyond industrial compostability to encompass broader environmental impacts.
PHAs, produced via bacterial fermentation of organic feedstocks, are witnessing increased traction from specialty film producers looking to align with stringent global sustainability protocols. Companies such as Danimer Scientific and RWDC Industries are accelerating innovation and commercialization, positioning PHA as a next-generation solution that satisfies both end-of-life flexibility and the need for performance-critical multilayer film applications in niche packaging sectors.
Application Insights
Based on application, the food packaging segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 60.32% in 2024. Within the food packaging domain, compostable multilayer films are gaining strong momentum due to evolving retail demands and packaging legislation targeting non-recyclable flexible formats.
A key driver is the push from major grocery chains and food brands to integrate circular economy principles-reducing contamination in organic waste streams while maintaining food shelf life and safety. In countries such as Germany, France, and Canada, regulatory incentives and extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes are further encouraging the transition toward compostable alternatives for packaging ready meals, snacks, and produce. These films offer a dual benefit: they serve as primary packaging and, post-consumer, can be composted alongside food waste, reducing sorting complexity and landfill dependency.

In the personal care segment, compostable multilayer films are gaining attention as brands seek clean-label, non-toxic, and environmentally aligned packaging to reflect their product ethos. A unique driver for this segment is the consumer preference for holistic sustainability-extending beyond product formulations into packaging transparency and biodegradability.
Startups and premium brands in skincare, organic cosmetics, and hygiene products are incorporating compostable films for sachets, pouches, and sample packs to enhance their ESG profile and meet retailer-driven sustainability thresholds. This shift is particularly visible in regions like Western Europe and South Korea, where eco-certification of both product and packaging is becoming a critical determinant of shelf space and consumer trust.
Regional Insights
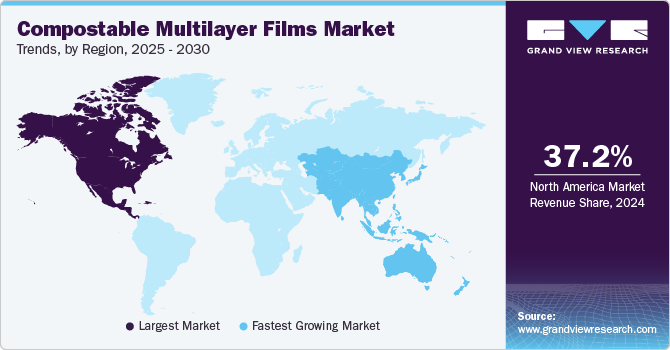
North America dominated the compostable multilayer films market with the largest revenue share of 37.24% in 2024. One of the core drivers accelerating the market in North America is the rise of green procurement policies across municipal, state, and federal levels. Governments are increasingly mandating compostable packaging solutions for food service, institutional catering, and event-based applications, particularly for single-use formats. States such as California, Washington, and New York are actively rolling out organics diversion mandates that necessitate certified compostable packaging in public-sector operations and waste management infrastructure. These directives are encouraging packaging suppliers and brand owners to shift towards multilayer compostable formats that align with localized composting capabilities, ensuring compatibility with food waste disposal streams and reducing contamination in curbside compost bins.
U.S. Compostable Multilayer Films Market Trends
The compostable multilayer films market in the U.S. accounted for the largest market revenue share in North America in 2024. A pivotal driver for the market is the proliferation of state-level Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws targeting packaging waste. States like California (SB 54), Oregon (SB 582), and Colorado have enacted frameworks that shift financial responsibility for waste management onto producers, incentivizing them to adopt lower-impact, compostable materials in place of complex multilayer plastics that are uneconomical to recycle. This regulatory shift is compelling large-scale converters and FMCG brands to redesign packaging portfolios with certified compostable multilayer films that can be processed in the growing number of municipal composting facilities. The legislation is not only altering cost structures but also pushing innovation in film barrier properties to meet functional and compliance needs simultaneously.
Europe Compostable Multilayer Films Market Trends
The compostable multilayer films market in Europe is being propelled by advanced technological integration of bio-based coatings and high-barrier layers that meet both compostability and performance standards. With the EU Green Deal and Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) setting ambitious sustainability benchmarks, converters across Germany, France, and the Netherlands are investing in multi-functional compostable film architectures for high-moisture and oxygen-sensitive goods. There is a notable surge in R&D focused on integrating cellulose, starch-based resins, and PVOH with PLA or PBAT substrates to deliver functional parity with conventional laminates. These efforts are reinforced by consumer pressure for plastic-free labeling and retailer-led zero-waste initiatives, creating a high-demand environment for next-generation multilayer compostable formats.
Asia Pacific Compostable Multilayer Films Market Trends
The compostable multilayer films market in Asia Pacific is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. A key driver for this market is the region-wide push toward bioeconomy development, with government-backed initiatives supporting local biopolymer production and end-use packaging applications. Countries like India, China, and Thailand are offering tax incentives, funding R&D clusters, and establishing bio-refineries aimed at reducing import dependency and boosting the availability of domestic feedstocks for PLA, PBS, and starch blends. In addition, growing pressure to manage plastic waste in urban centers has led to strict bans on multilayer plastics in cities such as Delhi, Jakarta, and Manila-creating a regulatory vacuum now being filled by compostable alternatives. The simultaneous development of localized material supply chains and waste processing capacity is giving multilayer compostable films a competitive edge across both export-driven and domestic FMCG segments.
Key Compostable Multilayer Films Company Insights
The compostable multilayer films industry is highly competitive, with several key players dominating the landscape. Major companies include Tipa Corp, Kuraray Co., Ltd., Futamura, Taghleef Industries, BASF SE, Novamont, Earthfirst Films, and Amcor plc. The market is characterized by a competitive landscape, with several key players driving innovation and market growth. Major companies in this sector are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability of their types.
Key Compostable Multilayer Films Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the compostable multilayer films market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Tipa Corp
- Kuraray Co., Ltd.
- Futamura
- Taghleef Industries
- BASF SE
- Novamont
- Amcor plc
- Earthfirst Films
Recent Developments
-
In November 2024, Earthfirst Films, a leading manufacturer of bio-material films, launched its Earthfirst Compostable Laminations. The company introduced unprinted, regenerative pre-laminations that are engineered for high barrier performance and designed for digital printing. This move was driven by demand from small and medium-sized brands seeking sustainable packaging solutions.
-
In October 2024, Material innovation company Sway announced that four fashion brands-Prana, Faherty, Alex Crane, and Florence-would use its compostable poly bags made from seaweed, plants, and compostable polymers. These bags, printed with algae-derived ink, are designed to degrade in both home and industrial compost environments.
Compostable Multilayer Films Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 1.54 billion
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 2.45 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 9.7% from 2024 to 2030
Base year for estimation
2024
Historical data
2018 - 2023
Forecast period
2025 - 2030
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million/billion, volume in kilotons, and CAGR from 2025 to 2030
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends
Segments covered
Material type, application, region
Regional scope
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central & South America; Middle East & Africa
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; Germany; UK; France; Italy; Spain, China; India; Japan; South Korea; Australia; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; South Africa; UAE
Key companies profiled
Tipa Corp; Kuraray Co., Ltd.; Futamura, Taghleef Industries; BASF SE; Novamont, Earthfirst Films; Amcor plc
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analyst’s working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Global Compostable Multilayer Films Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global compostable multilayer films market report based on the material type, application, and region:
-
Material Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, Volume, Kilotons, 2018 - 2030)
-
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
-
PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates)
-
Starch-based Films
-
Cellulose-based Films
-
Others
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, Volume, Kilotons, 2018 - 2030)
-
Food Packaging
-
Personal Care
-
Pharmaceuticals
-
Agriculture
-
Others
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, Volume, Kilotons, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
Australia
-
-
Central & South America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
South Africa
-
UAE
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global compostable multilayer films market size was estimated at USD 1.42 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1.54 billion in 2025.
b. The global compostable multilayer films market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.68% from 2025 to 2030 to reach USD 2.45 billion by 2030.
b. Food packaging dominated the compostable multilayer films market across the application segmentation in terms of revenue, accounting for a market share of 60.32% in 2024. Within the food packaging domain, compostable multilayer films are gaining strong momentum due to evolving retail demands and packaging legislation targeting non-recyclable flexible formats.
b. Some key players operating in the compostable multilayer films market include Tipa Corp, Kuraray Co., Ltd., Futamura, Taghleef Industries, BASF SE, Novamont, Earthfirst Films, and Amcor plc.
b. Growing consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging is pushing brands to adopt compostable multilayer films. Companies are using this shift to strengthen their sustainability image and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We offer custom report options, including stand-alone sections and country-level data. Special pricing is available for start-ups and universities.
Request Customization![Certified Icon]()
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."





